In this article, I am going to share with you an Ultimate Guide to technical SEO.
In this article You will learn:
XML sitemaps
Robots.txt
Duplicate content
Page load speed
Mobile responsiveness
Structured data markup
HTTPS/SSL
Google Search Console and its issues
And Much More.
If you are a beginner and want to rank your website at the top of the search engines.
You should read this complete technical SEO guide.
Fundamentals of Technical SEO
In this chapter I will be walking through the fundamentals of technical SEO You should know in 2023.

So If you are a beginner then you should read this complete chapter. Let’s dive right in.
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to optimizing a website’s technical elements to improve its search engine visibility and performance.
This includes optimizing website structure, navigation, URL structure, site speed, mobile-friendliness, and other technical aspects that impact how search engines crawl, index, and rank a website.
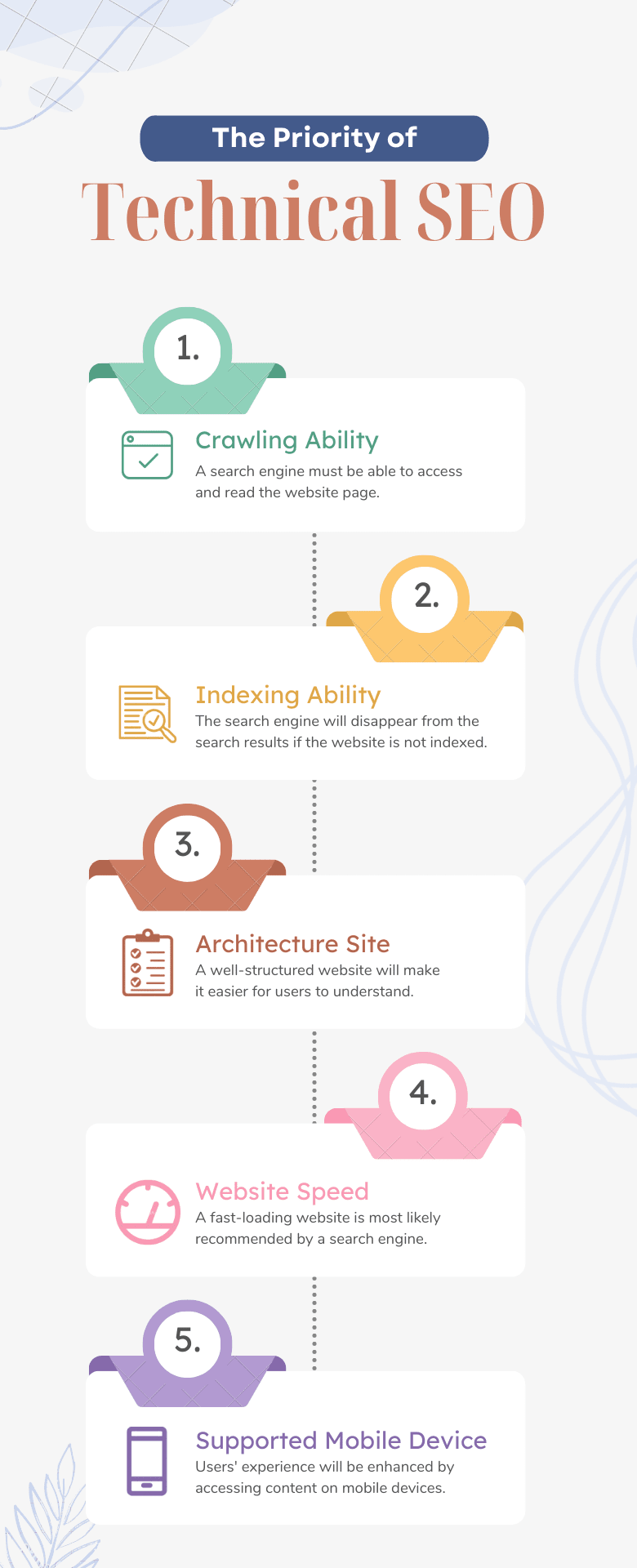
Why Is Technical SEO Important?
Technical SEO is of paramount importance as it directly impacts how search engines crawl, index, and rank a website.
It involves optimizing the technical elements of a website to ensure its visibility and performance in search results, affecting its organic traffic, search engine rankings, and overall online presence.

One of the primary reasons technical SEO is crucial is that it helps search engines understand a website’s content and structure.
Properly optimized technical elements, such as clean URL structures, accurate meta tags, and header tags, help search engines interpret a website’s relevance and authority, leading to better rankings.
Technical SEO also ensures that a website is easily accessible and user-friendly.
Factors such as site speed, mobile-friendliness, and responsive design significantly affect user experience, directly affecting website engagement, bounce, and conversion rates.
![]()
A website that loads quickly, displays well on various devices, and provides a smooth user experience is more likely to retain visitors and encourage them to stay longer, ultimately leading to higher conversions.
And also, Issues such as broken links, duplicate content, and incorrect redirects can negatively impact a website’s search engine rankings and visibility. And the list goes on and on. Let’s go through the steps to optimize your website without wasting time and energy.
How to Improve Your Technical SEO
Follow these steps to implement the points on your website.
Ensure to understand and follow everyone I covered in this definitive guide to technical SEO.
Connecting Website with Google Analytics
It is a crucial part of SEO.
Why?
Because Connecting your website with Google Analytics allows you to track and analyze various aspects of your website’s performance, such as traffic, user behaviour, conversions, and more.
Here are the steps to connect your website with Google Analytics.
- Sign up for Google Analytics: Go to the Google Analytics website and create a new account.
- Create a Property: Once you have an account, create a property in Google Analytics representing your website.
- Get the Tracking Code: You will receive your website’s unique tracking code (UA code) after creating a property.
- Add the Tracking Code to Your Website: Modify the HTML code of your website’s pages by adding the tracking code to the head section of your HTML document.
- Verify Your Tracking Code: Check the status of your tracking code in Google Analytics to ensure it’s receiving data.
Website Structure and Navigation
In this chapter, I will talk about website architecture and breadcrumbs.

So If you are a beginner then you should read this complete chapter. Let’s dive right in.
Website Structure
Website structure plays an important role in technical SEO. What exactly it is? Let’s go through it step by step.
Your Website Should look like this.

Let’s briefly talk about the actions you can take.
For example, this is the homepage of your website.
Then What about other pages on your website?
For example, if you are a digital agency. Your pages are:
Portfolio, Clients, Projects, Services, Blog Etc
These are the main pages that your website has. So now you need to try these pages around your homepage.
This can be done by adding Menu and Submenu to your site.

But What about the E-commerce store? If you have 1000+ products then how can you structure them?
Now I should say add products in your category pages and categories pages links on your homepage like this.

Your site pages should be 1-2 clicks away from your homepage. I hope you got the idea.
Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs, also known as breadcrumb navigation or breadcrumb trail, is a type of website navigation that provides users with a hierarchical or linear visual representation of their current location within a website’s structure. Breadcrumbs typically appear near the top of a webpage and are usually displayed horizontally or vertically as a series of clickable links.
The term “breadcrumbs” is derived from the story of Hansel and Gretel, in which the characters left a trail of breadcrumbs to find their way back home. Similarly, website breadcrumbs help users understand their current location within a website and provide an easy way to navigate back to higher-level pages or sections.
Breadcrumbs typically consist of a series of links that represent the path from the homepage or the top-level category to the current page. For example, a breadcrumb trail for a product page on an e-commerce website might look like this:
Home > Electronics > Smartphones > Apple iPhone X
Each link in the breadcrumb trail is typically clickable, allowing users to quickly navigate to any of the higher-level pages or sections in the hierarchy.
There are several types of breadcrumbs commonly used on websites:
Location-based breadcrumbs: These show the hierarchical structure of the website and the user’s current location within it, as shown in the example above.
Attribute-based breadcrumbs: These show the attributes or filters applied by the user to refine the content on the current page. For example, on a website selling clothes, a breadcrumb trail might show the selected attributes like “Men’s > Shirts > Casual > Blue”.
History-based breadcrumbs: These show the user’s browsing history within the website, allowing them to retrace their steps and quickly return to previously visited pages.
Breadcrumbs can provide several benefits to website usability and user experience, including improved navigation, better orientation within a website’s structure, and quicker access to higher-level pages or sections. Breadcrumbs can also help search engines understand the website’s structure and improve SEO (search engine optimization) by providing contextual information about the page’s location within the site.
Google Search Console Issues Explained
In this chapter, I will discuss all issues related to the google search console. You will find the solutions in them.

So If you want to solve your issues you should read this. Let’s dive right in.
Google Search Console is the most important part of a technical SEO campaign.
If you have issues with your website this will help you to find and fix these errors.
You can easily identify the errors on your website.
Let’s talk deeply about these issues and solve them.
1: Security Issues
This is the crucial issue of your website. You shouldn’t skip this issue. These are the 5 common reasons for security issues.
Unauthorized access: If an unauthorized user gains access to your Google Search Console account, they could potentially manipulate your website’s data, submit spammy content, or even remove your site from Google’s search results.
Phishing attacks: Phishing attacks can involve fake emails or websites that trick users into providing their Google Search Console login credentials, leading to unauthorized access to the account.
Malware or hacking: If your website or server is compromised with malware or gets hacked, it could potentially impact the security of your Google Search Console account, as the account is linked to your website’s data and settings.
Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks: XSS attacks occur when malicious scripts are injected into a website, which could potentially affect Google Search Console if the scripts manipulate or steal data from the account.
Social engineering attacks: Social engineering attacks involve manipulating individuals to divulge sensitive information, such as Google Search Console login credentials, through deception or manipulation.
I hope you have identified the issues. After identifying you can solve them. Remember you should try to solve these issues as soon as possible.
Page with redirect
A “Page with redirect issue” typically refers to a webpage that has a redirect implemented incorrectly or in a way that may cause issues with search engine optimization (SEO) or user experience.
Redirects are instructions that automatically direct web browsers from one URL to another. They are commonly used for various purposes, such as redirecting users from old URLs to new ones after a website migration, consolidating duplicate content, or redirecting broken links.
However, if redirects are implemented incorrectly or misconfigured, they can lead to problems that can impact SEO and user experience. Some common issues with page redirects include:
Redirect loops: A redirect loop occurs when a chain of redirects continuously redirects users from one URL to another in an infinite loop, preventing users from reaching the intended destination and causing a poor user experience.
Slow page load times: If redirects are not optimized or implemented inefficiently, they can add extra load time to a webpage, potentially resulting in slow page load times, which can negatively affect user experience and SEO.
Loss of link equity: Redirects can also impact the distribution of link equity (i.e., SEO value) from the original URL to the redirected URL. If implemented incorrectly, link equity may not pass effectively, resulting in a potential loss of SEO value for the redirected page.
Incorrect redirect type: There are different types of redirects, such as 301 (permanent) and 302 (temporary), each serving different purposes. Using the wrong type of redirect can result in incorrect indexing or caching by search engines, leading to SEO issues.
Broken or outdated redirects: If a redirect is pointing to a URL that no longer exists or has changed, it can result in broken links or outdated content, leading to a poor user experience and potentially impacting SEO.
It’s important to ensure that redirects are implemented correctly, using best practices, and regularly reviewed to avoid potential issues with page redirects.
Properly implemented redirects can help maintain SEO value, preserve user experience, and ensure that visitors reach the correct destination URL.
If you suspect issues with redirects on your website, it’s recommended to review and update them accordingly or seek assistance from a qualified SEO professional.
Alternative page with proper canonical tag
An “Alternative page with the proper canonical tag” refers to a webpage that is designated as an alternative version of another page on a website, and includes a canonical tag that indicates the preferred or canonical version of the content.
When implementing an alternative page with a proper canonical tag, You should follow the following steps. So let’s get started:
Identify the duplicate or similar content: Determine which pages on your website have similar or duplicate content that you want to consolidate.
Create the alternative page: Create a single preferred version of the content that you want to designate as the canonical version. This could involve merging content from multiple pages or creating a new page with the consolidated content.
Implement the canonical tag: On the alternative page, include a canonical tag in the HTML header, specifying the URL of the preferred or canonical version of the content. An example of this is given below.
<link rel=”canonical”
href=”https://www.example.com/
preferred-page”>
Update links and references: Update any internal links, references, or sitemaps to point to the preferred or canonical version of the content, rather than the duplicate or similar pages.
Monitor and verify: Regularly monitor and verify that the canonical tags are correctly implemented and functioning as intended. Use tools like Google Search Console or third-party SEO auditing tools to check for any potential issues or errors.
Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag
“Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag” refers to webpages on a website that have been intentionally excluded from being indexed by search engines using the ‘noindex’ meta tag. The ‘noindex’ meta tag is an HTML meta tag that can be added to the header of a webpage to instruct search engines not to index that particular webpage.
You can do this for different reasons, such as preventing duplicate content from being indexed, hiding low-quality or temporary pages from search results, or keeping private or sensitive information hidden from public search results.
However, if webpages are unintentionally or mistakenly tagged with ‘index’, it can lead to issues with search engine visibility and indexing, potentially resulting in decreased organic search traffic and visibility. To solve the issue of webpages being excluded by the ‘noindex’ tag, you can follow the steps below:
Review ‘noindex’ tags: Conduct a thorough review of the ‘noindex’ meta tags on your web pages to identify any unintentional or incorrect usage. Check the HTML header of each webpage to ensure that the ‘noindex’ meta tag is not present or has been intentionally added for valid reasons.
Update ‘noindex’ tags: If you identify any unintentional or incorrect usage of ‘no index’ tags, update the HTML header of the affected webpages to remove the ‘noindex’ meta tag or replace it with the appropriate indexing instruction, such as ‘index’ for allowing indexing or ‘follow’ for allowing indexing and following links.
Verify changes: After making changes to the ‘no index’ tags, verify that the changes have been correctly implemented by checking the HTML source code of the webpages or using tools like Google Search Console or third-party SEO auditing tools to confirm that the ‘noindex’ tag has been removed or updated.
Submit to search engines: If the webpages were previously excluded by ‘noindex’ tags, submit the updated webpages to search engines for re-indexing. This can be done through the search engine’s submission or indexing request tools, such as Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools.
Monitor and maintain: Regularly monitor the ‘no-index’ tags on your web pages to ensure that they are correctly implemented and maintained over time. Conduct regular audits and reviews to identify and fix any potential issues or mistakes.
It’s important to ensure that ‘noindex’ tags are used intentionally and judiciously, following best practices, and regularly reviewed to avoid potential issues with search engine visibility and indexing. Properly managing ‘noindex’ tags can help improve the SEO performance and visibility of your website in search results. If you’re unsure about the usage of ‘no index’ tags on your website, consulting with an experienced SEO professional can be beneficial.
Duplicate without user-selected canonical
Duplicate without user-selected canonical” refers to duplicate content issues on a website where a preferred or canonical version of the content has not been explicitly selected or specified by the website owner or user. Canonicalization is the process of indicating the preferred version of a webpage when there are multiple versions of similar or duplicate content. User-selected canonical refers to the explicit designation of a preferred version of content by the website owner or user.
Duplicate content can occur on websites in various ways, such as through multiple URLs with identical or similar content, URL variations, session IDs, print-friendly pages, or HTTP vs. HTTPS versions of the same content. When a preferred or canonical version of the content has not been explicitly selected or specified, search engines may not be able to determine the most authoritative version of the content, leading to potential issues with search engine visibility, indexing, and rankings.
To solve the issue of duplicate content without user-selected canonical, you can follow the steps below:
Identify duplicate content: Conduct a thorough audit of your website to identify duplicate content pages or variations that are causing the issue. This can involve checking for duplicate URLs, URL parameters, session IDs, or other similar content that may be causing duplicate content problems.
Evaluate content variations: Evaluate the different variations of content and determine which version should be the preferred or canonical version. Consider factors such as content quality, relevance, user experience, and business goals to make an informed decision.
Implement canonical tags: Once you have determined the preferred or canonical version of the content, implement canonical tags on the duplicate content pages, pointing to the preferred version. Canonical tags are HTML tags that indicate to search engines the preferred version of a webpage. For example:
bash
Copy code
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/
preferred-page”>
Verify canonical tags: Verify that the canonical tags are correctly implemented and functioning as intended. Use tools like Google Search Console or third-party SEO auditing tools to check for any potential issues or errors.
Monitor and maintain: Regularly monitor your website for any new instances of duplicate content and ensure that the canonical tags are correctly implemented and maintained over time. Conduct regular audits and reviews to identify and fix any potential issues or mistakes.
By implementing user-selected canonical tags on duplicate content pages, you can help search engines understand the preferred version of the content, consolidate authority, and avoid potential duplicate content issues. It’s important to follow best practices and ensure that canonical tags are implemented correctly to effectively address the issue of duplicate content without user-selected canonical. If you’re unsure about canonicalization or duplicate content issues on your website, consulting with an experienced SEO professional can be beneficial.
Discovered – currently not indexed
Discovered – currently not indexed” is a status in Google Search Console that indicates that Google has discovered a webpage during its crawling process but has not yet indexed it. This means that while Googlebot, Google’s web crawler, has found the webpage during its crawl, it has not yet included it in its search index, and therefore the webpage is not currently appearing in Google’s search results.
There can be several reasons why a webpage is marked as “Discovered – currently not indexed” in Google Search Console:
New or recently updated content: If the webpage is new or has been recently updated, it may take some time for Google to index it. Googlebot needs to crawl the webpage, analyze its content, and add it to its search index before it can start appearing in search results.
Low-priority or low-quality content: Google prioritizes the indexing of high-quality and relevant content. If the webpage has low-quality or thin content, duplicate content, or other issues that make it less valuable or relevant, Google may not index it.
Technical issues: There may be technical issues with the webpage that prevent Google from indexing it, such as crawl errors, noindex meta tags, or other indexing directives that block Googlebot from indexing the page.
Indexing delays: Google’s indexing process is not instant, and there may be delays in indexing new or updated content due to various factors, including server load, crawling priorities, and algorithmic changes.
To address the issue of “Discovered – currently not indexed”, you can take the following steps:
Verify content quality: Ensure that the content on the webpage is high-quality, unique, and relevant to users. Avoid duplicate content, thin content, or other low-quality content issues that may hinder indexing.
Review technical issues: Check for any technical issues that may prevent Googlebot from indexing the webpage, such as crawl errors, noindex meta tags, or other indexing directives. Fix any issues that may be blocking indexing.
Monitor indexing status: Keep an eye on the indexing status in Google Search Console to track changes and updates. If the status remains unchanged for an extended period, consider re-submitting the webpage for indexing or investigating further.
Follow best practices: Follow SEO best practices, such as using descriptive and unique title tags, optimizing meta tags, using descriptive URLs, and creating a sitemap, to help Googlebot understand the content and improve the chances of indexing.
Be patient: Indexing delays can occur, and it may take some time for Google to index new or updated content. Be patient and continue to monitor the indexing status over time.
It’s important to note that not all webpages discovered by Google will necessarily be indexed, as Google uses various algorithms and criteria to determine which pages to include in its search index. However, by ensuring content quality, resolving technical issues, and following SEO best practices, you can increase the likelihood of your web pages being indexed and appearing in Google’s search results. If you’re facing persistent issues with indexing, consulting with an experienced SEO professional may be helpful.
Crawled – currently not indexed
Crawled – currently not indexed” is a status in Google Search Console that indicates that Googlebot, Google’s web crawler, has crawled a webpage during its crawling process, but has not yet indexed it. This means that Googlebot has visited the webpage, and analyzed its content, but has not yet included it in its search index, and therefore the webpage is not currently appearing in Google’s search results.
There can be several reasons why a webpage is marked as “Crawled – currently not indexed” in Google Search Console:
New or recently updated content: If the webpage is new or has been recently updated, it may take some time for Google to index it. Googlebot needs to crawl the webpage, analyze its content, and add it to its search index before it can start appearing in search results.
Low-priority or low-quality content: Google prioritizes the indexing of high-quality and relevant content. If the webpage has low-quality or thin content, duplicate content, or other issues that make it less valuable or relevant, Google may not index it.
Technical issues: There may be technical issues with the webpage that prevent Google from indexing it, such as crawl errors, noindex meta tags, or other indexing directives that block Googlebot from indexing the page.
Indexing delays: Google’s indexing process is not instant, and there may be delays in indexing new or updated content due to various factors, including server load, crawling priorities, and algorithmic changes.
To address the issue of “Crawled – currently not indexed”, you can take the following steps:
Verify content quality: Ensure that the content on the webpage is high-quality, unique, and relevant to users. Avoid duplicate content, thin content, or other low-quality content issues that may hinder indexing.
Review technical issues: Check for any technical issues that may prevent Googlebot from indexing the webpage, such as crawl errors, noindex meta tags, or other indexing directives. Fix any issues that may be blocking indexing.
Monitor indexing status: Keep an eye on the indexing status in Google Search Console to track changes and updates. If the status remains unchanged for an extended period, consider re-submitting the webpage for indexing or investigating further.
Follow best practices: Follow SEO best practices, such as using descriptive and unique title tags, optimizing meta tags, using descriptive URLs, and creating a sitemap, to help Googlebot understand the content and improve the chances of indexing.
Be patient: Indexing delays can occur, and it may take some time for Google to index new or updated content. Be patient and continue to monitor the indexing status over time.
It’s important to note that not all webpages crawled by Googlebot will necessarily be indexed, as Google uses various algorithms and criteria to determine which pages to include in its search index. However, by ensuring content quality, resolving technical issues, and following SEO best practices, you can increase the likelihood of your web pages being indexed and appearing in Google’s search results. If you’re facing persistent issues with indexing, consulting with an experienced SEO professional may be helpful.
Duplicate, Google chose a different canonical than the user
Duplicate, Google chose a different canonical than the user” is a status in Google Search Console that indicates that Google has identified duplicate content on different webpages, and has chosen a different canonical URL than what the user has specified.
The canonical tag is an HTML tag used by website owners to indicate the preferred version of a webpage when there are multiple versions of similar or duplicate content. It helps search engines understand which version of a webpage should be considered the primary or canonical version for indexing and ranking purposes.
However, in some cases, Google may choose a different canonical URL than what the website owner has specified. This can happen due to various reasons, such as Google’s algorithmic analysis of the content and other signals it uses to determine the most relevant version of the content.
When Google chooses a different canonical URL than what the user has specified, it means that Google has determined that a different version of the content should be considered as the primary or canonical version for indexing and ranking. This can potentially impact how the webpage is displayed in Google’s search results and may affect its visibility and ranking.
To address the issue of “Duplicate, Google chose a different canonical than the user” in Google Search Console, you can take the following steps:
Review canonical URL implementation: Double-check that you have correctly implemented the canonical tags on your web pages and that they point to the correct and preferred version of the content. Make sure that the canonical URL matches the actual URL of the page that you want to be considered as the canonical version.
Verify content similarity: Review the content on the webpages that are marked as duplicates and ensure that they are indeed similar or duplicate versions of each other. If there are differences in content or other factors that make them distinct, consider making necessary updates to make them more unique.
Check for other signals: Consider other factors that may be influencing Google’s decision on the canonical URL, such as internal linking, external linking, URL structure, and user engagement signals. Make sure that these factors are aligned with your intended canonical URL.
Monitor for changes: Keep an eye on the “Duplicate, Google chose a different canonical than the user” status in Google Search Console and monitor for changes over time. If the issue persists, consider seeking further assistance from SEO professionals or reaching out to Google for clarification.
It’s important to ensure that your website follows best practices for canonicalization and has unique, high-quality content to avoid duplicate content issues. By addressing any discrepancies between the canonical URLs you’ve specified and what Google has chosen, you can help improve the indexing and ranking of your web pages in Google’s search results.
Website Ranking Points
In this chapter, I will website ranking points like UX design, mobile optimization, and much more

So If you are a beginner then you should read this complete chapter. Let’s dive right in.
Website UI and UX Design
User experience plays a very important role in your website’s success.
You should have to consider your website design.
Why?
Because when you have good design people will spend more time on your website.
When more people spend more time it gives you the signal to Google that this is the best website. And it helps you to rank high.
Make sure your website should have One Version.
Some people don’t know whether their website has one version or not.
First, we should know what it is.
When you add www to your website.
Is it redirecting to the same page?
Let’s take an example. For example, your website URL is this:
Homepage
Then you should try this URL
Homepage
If these both URLs go to the same page then it’s fine if not then you should add redirects to your website.
WHY?
because when a website has 2 URLs crawlers will confuse which one is right and which one is wrong.
You should try these URLs to know that your website has one version.
You should consider the following URLs to check.
http://yoursite.com
https://yoursite.com
http://www.yoursite.com
https://www.yoursite.com.
AMP Version of your Website
The AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) version of a website refers to a stripped-down, simplified version of the website’s content that is optimized for fast loading on mobile devices. AMP is an open-source project by Google that aims to improve the performance and user experience of webpages on mobile devices.
AMP pages are designed to load quickly and provide a seamless browsing experience, especially for users accessing websites on slower internet connections or using mobile devices with limited processing power. They typically have a minimalistic design and are stripped of certain elements that can slow down webpage loading times, such as JavaScript, third-party scripts, and heavy media files.
To create an AMP version of a website, webmasters need to use a specific set of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code that adheres to the rules and guidelines set forth by the AMP project. This allows search engines, including Google, to recognize and serve the AMP version of webpages to mobile users when applicable.
The AMP version of a website is often denoted by a specific URL structure, typically using the “https://example.com/amp/” format, where “example.com” is the domain name of the website. When users access a webpage from a mobile device, they may be automatically redirected to the AMP version of the webpage if available.
Implementing AMP on a website can have benefits such as improved mobile performance, better visibility in search results (as Google may give preference to AMP pages in mobile search results), and enhanced user experience for mobile users. However, it also requires careful consideration and implementation to ensure that the AMP version is consistent with the branding, content, and functionality of the main website.
Website security
Website security is an important part of Technical SEO.
If your website isn’t secured you will lose your website.
For securing your website you can install the SSL certificate that I mentioned above and use the plugin called:
Sucuri Security – Auditing, Malware Scanner, and Hardening.
HTTPS and SSL
Do you know?
According to a study, as of 2021, over 90% of websites on the first page of Google search results are HTTPS secure.
Google also considers HTTPS as a ranking factor, and websites that are not HTTPS may experience a drop in rankings.
Both of these are important. Here first we talk about HTTPS.
Think for a minute if your website looks like this.

Who will visit your website and buy the product or service?
Off course no one.
Then how can you add HTTPS to your website? Here is what you should do.
- Install an SSL certificate on your website.
WHY?
Because it helps your website to be secure
WHY?
Hackers try to hack your website so that’s why your website should have an SSL certificate.
If you are using WordPress then in your hosting automatically you get Free SSL but in Blogger you need to buy it separately.
Website Speed Optimization
In this chapter, I will be walking through the page speed of speed. How you can improve and find it. And much more.

So If you are a beginner then you should read this complete chapter. Let’s dive right in.
Mobile Optimization
In this period everyone uses mobile and knows how important it is for the website of having mobile friendly.
Mobile devices now account for more than 70% of global web traffic, according to techjury.net.

But did you know that 5 years ago there was no such a big thing as having a mobile-friendly website?
But from time to time people started to use mobiles across the world.
Then search engines came into action.
Google has launched a new algorithm and says the website should be mobile-friendly.
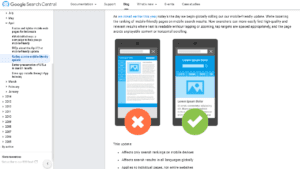
Without mobile friendliness, you are not going to rank. So how can you optimize your website for mobile responsiveness?
Here are quick some steps you can do.
- Use Responsive Theme
- Design your website responsively.
- Use the AMP version for your blog posts
I hope you got the idea. Now let’s talk about speed optimization.
Page Speed Optimization
Page speed optimizations play a big role in website success. Do you know?
According to a study by Google, if a webpage takes more than 3 seconds to load, 53% of mobile users are likely to abandon the site.
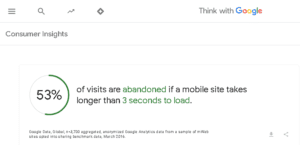
But people don’t know how to optimize. First, we should talk about why it’s important.
It’s important because as Google has cleared that sites that have a loading time of within 3 seconds tend to rank higher. But if your website is more than 3 seconds what should you do?
So let’s talk about what you can do. You can see your website speed on 3 different tools.
All these tools have their pros and cons.
But you should use three of these tools.
Now if you are using WordPress.
Optimizing Website Speed On WordPress
Then I should recommend you use these plugins to speed up your website.
- W3 Total Cache
- LiteSpeed
- Core Web vital
- Autoptimizer
- A3 lazy load
- Smush
You can’t use all these tools at the same time.
But you should try according to your website.
Still, if you are facing issues with optimization.
You should do these steps.
- Add Height and width of images
- Decrease animation on your website
- Compress your images
- Use loadable fonts
- Remove unused themes and plugins
You can also take our services to optimize your website speed.
URL Optimization
URL Optimization isn’t the compulsory part of technical SEO. But it’s. Here’s how.
Try to use short URLs in your pages and post.

I don’t recommend you go back and remove previous URLs but in the future.
You should use short URLs, Why? Because a recent study says that short URLs rank better than long URLs.
Image Optimization
Some people ignore image optimization. Even when we see on our client’s websites their images aren’t optimized and compressed.
It is compulsory to optimize your images,
Here is how.
Before publishing any image on your website you should use the tool called imagecompressor.com.
This will compress your images superbly.
Now if you are using WordPress you can use the plugins called Smush or Hummingbird.
I hope you got the idea.
Crawling and Indexing of Your Website
In this chapter, we will learn crawling and indexing points. like Robot.txt, sitemaps, and schema markeup.

Withou further let dive into it.
XML Sitemap
XML sitemap is a roadmap of your website. It helps crawlers easily find pages of your website. Your website must have an XML sitemap.
According to a study by Ahrefs, having an XML sitemap can help search engines discover and index new content on a website faster.
Now let’s talk about how to create a sitemap for your website.
First, go to the Google search console>Sitemaps.
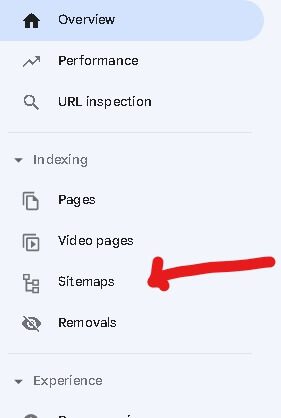
In many cases here are some different options. Some beginners are confused but don’t worry I will be helping you.
First If you have this interface then you should write this.
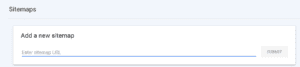
Then Write (http://yoursite.com/sitemap.xml).
If you have this interface.
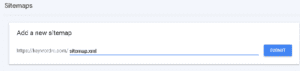
You should write this (sitemap.xml).
If you are running an e-commerce store then you should write this.
(https://www.YOURDOMAIN.com/
sitemap_index.xml).
I hope you got the idea.
Robots.txt File
Robot.txt file help crawlers to index pages. I mean when crawlers visit your website.
It doesn’t know which page should and which shouldn’t index.
But if you have a Robot.txt file it says crawlers to index the right page.
Now let’s talk about how to add this.
Adding Robot.txt file in WordPress
If you are using WordPress then you should have YOAST SEO Plugins or RANKMATH SEO Plugins. Here you should follow these steps.
In Yoast SEO.
Go to tools>File editor> Create a robot.txt file.
In rank math
Go to general Settings>Edit robot .txt.
But If you are using Blogger now you should follow these steps.
Adding Robot.txt file in Blogger
I should recommend you use this tool. SEOoptimer.
You will see the form here.
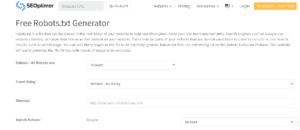
You need to fill out this form. Then after filling out the form you can download or Copy the file.
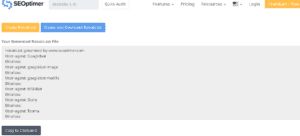
Then go to your blogger website.
Settings>Crawlers and indexing>Custom robot.txt.

Paste your file here and you should allow the options. I hope you got the idea.
Schema Markup
According to a study by Search Engine Journal, websites that use structured data can see up to a 30% increase in click-through rates (CTR) in search results.
Schema markup helps users easily find the content on your website.
For example when searching for something on Google like this.
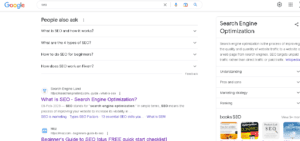
You will see the results like this.
Guess, what they are?
This is called schema markup.
It helps you a lot.
You can use tools like schemantra.com to generate schema.
If you are using WordPress you can install the plugin called Schema.
Other SEO Points
In this chapter, I will discuss some other SEO points. like duplicate content, conical URLs, broken link check and many more

Duplicate Content Check
Duplicate content is on the rise.
Everyone starts the website and tries to copy and paste the content from a website and waits for traffic.
Hey, you are not going to rank.
Nowadays the better version of copied content is AI writing tools.
Do you know?
How do AI content tools write content?
Off course from other websites on the internet. They just write content in their ways that’s why their content isn’t duplicated.
But think for a minute of Google E-E-A-T. Google has recently launched another E. This Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness are the guidelines of Google.
That is clear that the pages will rank on Google based on these things.
It’s, not the old school you just write content from other websites or AI tools and rank on Google.
This is just waist of time energy and money. You need to have experience and authority in your niche to write content.
By the way in the last, I should recommend you use the tool duplichecker.com for identifying duplicate content. Your content should be 0-9% duplicate out of 100.
Canonical URLs
Canonical URLs refer to the preferred URL that a website owner or webmaster specifies for a particular webpage when multiple URLs can access the same content.
Canonical URLs are used to consolidate the duplicate content issue and indicate to search engines the preferred version of a webpage that should be indexed and ranked.
Broken Link Check
Now you need to check if your website has broken links.
Why?
Because it’s bad for user experience and crawlers to crawl links on your website.
For checking broken links on your website you can use the Chrome extension called CheckMyLink.
After identifying them you should remove them.
Orphan or Zombie Pages
These are the pages that have low value.
It means they have low-quality content and aren’t getting traffic. These pages are useless.
You should consider deleting these pages from your website.
WHY?
Because the good pages you have the better chances to rank higher in Google.
You can check zombie pages on Google SERP. Just Enter this in Google.
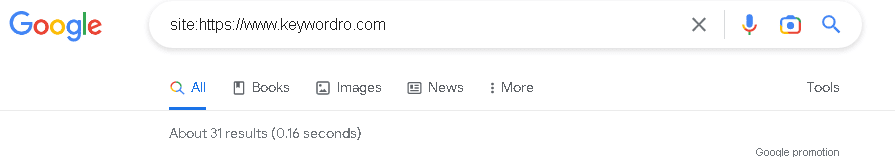
Site:Yoursite.com
You will see the all pages that your website has.
Tips for Technical SEO
In this chapter I will be walking through the tips for technical SEO You should know in 2023.

So If you are a beginner then you should read this complete chapter. Let’s dive right in.
Backlinks Quality
Having authority backlinks to your website is compulsory. If your website has low-value backlinks You are not going to rank.
So what are the low-value backlinks?
- Backlinks from irrelevant websites
- Backlinks from a low-authority website
- Backlinks from bad ways of link building techniques like
- PBN Sites
- Directory Submission website
- Spammy Blog comment sites
- Article Submission sites
- Classified submission sites
You should avoid having these types of links on your website.
You can check backlinks from Moz.com and UbberSuggest.
They will give you complete backlinks analysis reports. You can find the backlinks and remove them.
You can read this guide to remove backlinks.
Internal Links
Internal Links are very helpful for your website. You should have to increase the number of internal links on your website.
Why?
They help your website rank higher. But remember don’t try to overuse internal links.
Add naturally to your content.
Optimize Website for Local SEO
Optimizing a website for local SEO (Search Engine Optimization) involves implementing specific strategies and techniques to improve the website’s visibility and search engine rankings for local searches.
Here are some steps you can take to optimize your website for local SEO:
Use location-specific keywords:
Incorporate location-specific keywords into your website’s content, meta tags, and URL structure. This helps search engines understand that your website is relevant to local searches.
For example, if you have a bakery in New York City, use keywords like “New York City bakery” or “bakery in NYC” throughout your website.
Create and optimize your Google My Business (GMB) listing:
Google My Business is a free tool that allows businesses to manage their online presence on Google, including their appearance in local search results.
Create a GMB listing for your business and ensure it is complete and accurate with your business name, address, phone number, website, and business hours. Also, include photos, reviews, and relevant categories to optimize your GMB listing.
Include local business schema markup:
Schema markup is a type of structured data markup that helps search engines understand the content and context of your website.
Include local business schema markup on your website to provide search engines with information such as your business name, address, phone number, and reviews in a format that is easy for them to interpret.
Add Social Media Button on your website
Adding social media profiles helps users to build trust. If you have a social presence it’s the plus point.
Also, Google will see your social presence and your author bio.
Headings and subheadings of the website
On your website, your all pages and posts should have headings and subheadings.
If you haven’t your pages called will not rank on Google.
I should recommend you add keywords in your heading and subheadings.
I hope you have got the idea.
Titles and description
Titles play an important role in SEO. Titles can help you to get more traffic on your website.
how?
When people search for specific keywords. They might want to know about the topic.
If your title is engaging then people will click on it.
Here I will give you some tips to optimize your titles.
- Add Keywords at the beginning
- Use Current Year Like (2023)
- Use Numbers and Parenthesis
- Use These words Like (Guide, Ultimate, and Definitive).
Descriptions
But Do your descriptions also helpful in SEO? According to the research, google will change the descriptions of your pages according to users’ queries.
I mean if you set your description it will be removed by Google.
But I recommend you to add your description and add main keywords and LSI keywords in your description.
Conclusion
I hope you have learned totally about technical SEO. What steps you will take after reading this guide? Let me know in the comment below. If you have any questions or queries related to On-Page or Off-Page SEO leave a comment below.